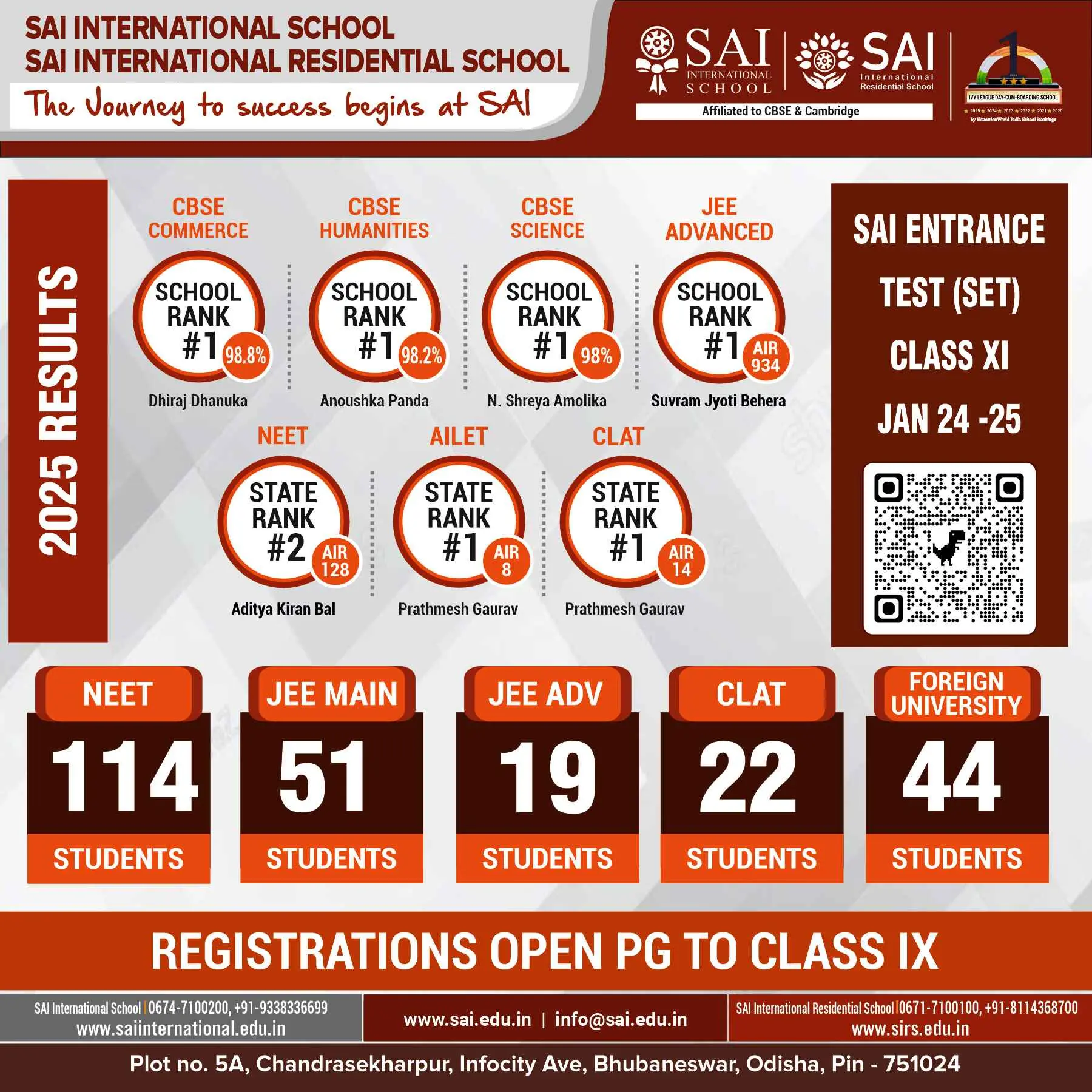
Bhubaneswar: The British Cemetery at Barabati, Balasore, one of oldest colonial era cemeteries of Odisha, is wallowing in neglect.
If this was not enough, anti-socials have converted this dilapidated and abandoned graveyard with 33 gravestones including spires and tombs, dating back to the 18th century, into their den and vandalised this historically important place by demolishing its compound wall, exposing the cemetery to the vagaries of street dogs and cattle.
Some of the marble head stones of the tombs have also been removed. The overgrown vegetation is also spelling the ruin of this heritage site.
For the British, Balasore was a favoured maritime centre. The strategic location of the place bordering the Bengal province had also drawn the Dutch, French and Portuguese maritime traders to this coastal town. Besides many merchants and mariners, the graveyard also has the tombstones of both Sir Henry Rickett, the first collector of Balasore (1827-36), his wife Lady Rickett. Lady Rickett died in Balasore while Sir Henry Rickett died in England in 1886. As per his last wish, his mortal remains were ferried by sea to this place and buried beside his wife grave. ‘Henry neither forgot Balasore nor Oriya’ is inscribed on the then British administrator’s tomb.
The cemetery also has the graves of, Captain Morgan who had freed Balasore from the Marathas and of Sir Francis Walter, the hero of British Royal Navy who led several battles in Madras, Goa, Harispur, Pipili port and Balasore. It also houses tombstones of five clergies. The inscriptions have corroded with the passage of time.
The cemetery was built between 1776 and 1881. The Indian National Trust for Art and Cultural Heritage (INTACH) had been entrusted to restore the old place a few years ago and a boundary wall was constructed with the MPLAD funds of Dr. Manmath Nath Das under the supervision of the then collector Ashwini Vaishnaw. INTACH, Balasore Chapter, has listed this site as a heritage site along with 73 other built heritages of the district and shared it with the district administration.
The future administration of British cemeteries in India had been repeatedly raised during the Transfer of Power before Independence. Before 1947, most were maintained by the local Executive Engineer in consultation with the local Chaplain. In 1949, the British Government decided not to support the maintenance of the European cemeteries in India and to leave the task of caring for the graveyards to the Christian congregations. The Governments of India had given assurances that they would protect cemeteries from destruction and desecration. A few graveyards were placed under the protection of the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) and of State authorities. However, many of these extraordinary legacies of British India lie strewn across the nation, most of them in forgotten, weed-covered cemeteries that have little or no future in modern India. These decaying colonial-era graveyards in India became targeted for conservation starting in the 1970s by the British Association for Cemeteries in South Asia (BACSA).
Uday Ranjan Das, the Convener of Intach’s Balasore Chapter has written to the district authorities to have the cemetery wall reconstructed and to have the place cleared of all vegetation.